Identifying Waste
- Waste is defined as non-value, or inefficient activity. Lean focusses on the removal of waste from a process to establish flow.
- Lean also promotes problems as opportunities for improvement as opposed to things which need to be fixed.
- Waste can be quite obvious in a process, but can also be challenging to remove as it is “the way it has always been done”.
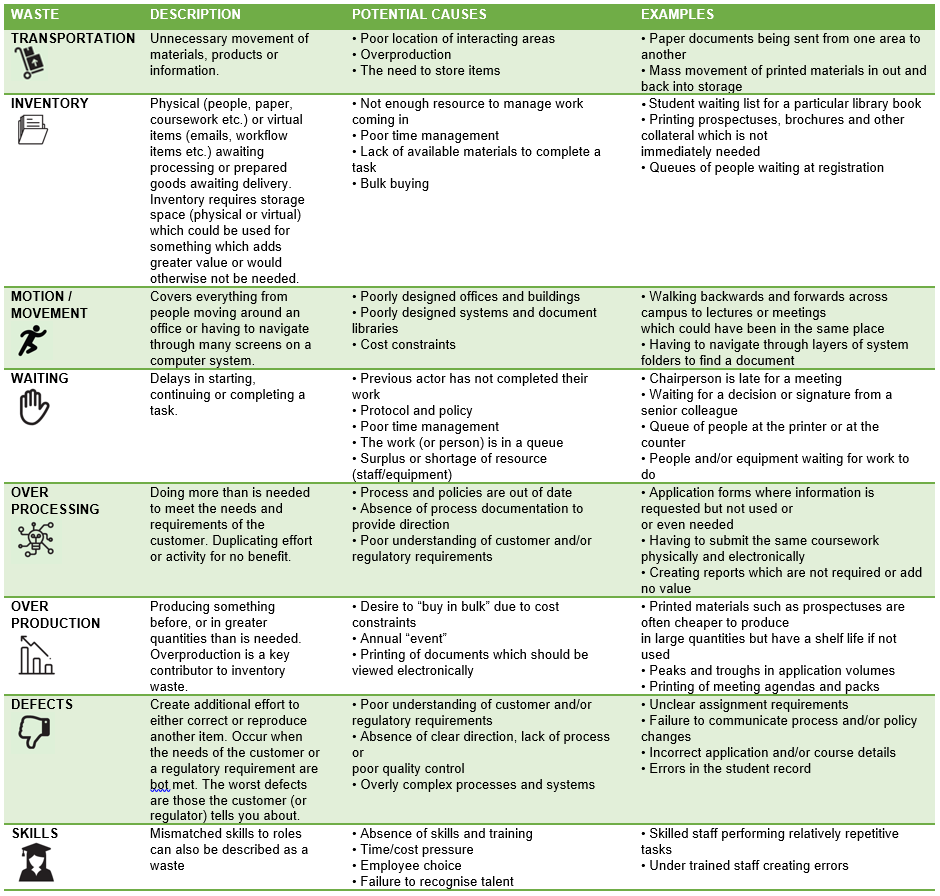
Transportation
Description
Unnecessary movement of materials, products or information.
Potential Causes
- Poor location of interacting areas
- Overproduction
- The need to store items
Examples
- Paper documents being sent from one area to another
- Mass movement of printed materials in, out and back into storage
Inventory
Description
Physical (people, paper, coursework etc) or virtual items (emails, workflow items etc.) awaiting processing or prepared goods awaiting delivery. Inventory requires storage space (physical or virtual) which could be used for something which adds greater value or would otherwise not be needed.
Potential Causes
- Not enough resource to manage work coming in
- Poor time management
- Lack of available materials to complete a task
- Bulk buying
Examples
- Student waiting list for a particular library book
- Printing prospectuses, brochures or other collateral which is not immediately needed
- Queues of people waiting at registration
Motion / Movement
Description
Covers everything from people moving around an office having to navigate through many screens on a computer system.
Potential Causes
- Poorly designed offices and buildings
- Poorly designed systems and document libraries
- Cost constraints
Examples
- Walking backwards and forwards across campus to lectures or meetings which could have been in the same place
- Having to navigate through layers of system folders to find a document
Waiting
Description
Delays in starting, continuing or completing a task.
Potential Causes
- Previous actor has not completed their work
- Protocol and policy
- Poor time management
- The work (or person) is in a queue
- Surplus or shortage of resource (staff / equipment)
Examples
- Chairperson is late for a meeting
- Waiting for a decision or signature from a senior colleague
- Queue of people at the printer or at the counter
- People and / or equipment waiting for work to do
Over Processing
Description
Doing more that is needed to meet the needs and requirements of the customer. Duplicating effort or activity for no benefit.
Potential Causes
- Process and policies are out of date
- Absence of process documentation to provide direction
- Poor understanding of customer and / or regulatory requirements
Examples
- Application forms where information is requested but not used or even needed
- Having to submit the same coursework physically and electronically
- Creating reports which are not required or add no value
Over Production
Description
Producing something before, or in greater quantities than is needed. Over production is a key contributor to inventory waste.
Potential Causes
- Desire to "buy in bulk" due to cost constraints
- Annual "event"
- Printing of documents which should be viewed electronically
Examples
- Printed materials such as prospectuses are often cheaper to produce in large quantities but have a shelf life if not used
- Peaks and troughs in application volumes
- Printing of meeting agendas and packs
Defects
Description
Create additional effort to either correct or reproduce another item. Occurs when the needs of the customer or a regulator are both met. The worst defects are those the customer (or regulator) tells you about.
Potential Causes
- Poor understanding of customer and / or regulatory requirements
- Absence of clear direction, lack of process or poor quality control
- Overly complex processes and systems
Examples
- Unclear assignment requirements
- Failure to communicate process and / or policy changes
- Incorrect application and / or course details
- Errors in the student record
Skills
Description
Mismatched skills to roles can also be described as a waste.
Potential Causes
- Absence of skills and training
- Time or cost pressure
- Employee choice
- Failure to recognise talent
Examples
- Skilled staff performing relatively repetitive tasks
- Under trained staff creating errors
Summary